Overview
Over-pronation is very common and affects millions of Australians. To better understand this condition, we'll take a closer look at the 3 most common foot types. An estimated 70% of the population has fallen arches (or a low arch). Only 20% has a normal arch. And 10% have abnormal feet, in other words they either have flat feet or the opposite - a high arched foot.
Causes
There are many different causes of flat feet, which can be separated into two main categories. The first category, congenital flat foot, is a condition that one is born with or is predisposed to at birth. This type includes the completely asymptomatic, pediatric flexible flat foot-by far the most common form of congenital flat foot. Flexible means that an arch is present until weight is put on the foot, at which time the arch disappears. This foot type is a result of the fact that all people are born with different physical features. Some people have bigger noses than others, just as some people have flatter feet (of course, there is no known correlation between the two). Any alteration in the many building blocks of the foot can influence its shape. At the other end of the spectrum, yet within the same category of congenital flat foot, exist several rare, more severe forms of flat foot. These severe conditions include Vertical Talus, Congenital Calcaneal Valgus, and Tarsal Coalitions - all of which are more rigid (no arch with or without weight on the foot) and definitely symptomatic. Luckily, these are much less common, but can usually be identified by specialists at the time of presentation and treated appropriately. The second category, acquired flat foot, develops over time, rather than at birth. Many different factors can contribute to the development of flat feet. These include the types of shoes a child wears, a child's sitting or sleeping positions, compensation for other abnormalities further up the leg, or more severe factors such as rupture of ligaments or tendons in the foot. Very commonly, the reason for flat feet is that the foot is compensating for a tight Achilles tendon. If the Achilles tendon is tight, then it causes the foot to point down, or to plantarflex (as occurs when stepping on the accelerator of your car). Even minimal amounts of plantarflexion can simulate a longer leg on that particular side, assuming that the other foot is in the normal position. The body therefore tries to compensate by pronating, or flattening out the arch, thereby making up for the perceived extra length on the affected side.
Symptoms
People will have a very heavily dropped arch and it won?t affect them at all and people will have it slightly dropped and it could cause fierce problems. It could cause things like plantar fasciitis, it could cause heel spurs, desperate ball-of-the-foot pressure, or pressure on the big toe known as the hallux which causes discomfort in the foot. It will create problems upwards to the knees, hips and the back once you?re out of line.
Diagnosis
Podiatrists are trained in expertly assessing flat feet and identifying different risk factors and the causes for it. Initial assessment will begin with a detailed history attempting to find out if any underlying illness has resulted in this. A detailed clinical examination normally follows. The patient may be asked to perform certain movements such as walking or standing on their toes to assess the function of the foot. Footwear will also be analysed to see if there has been excessive wear or if they are contributing to the pronation of the foot. To assess the structure of the foot further, the podiatrist may perform certain x-rays to get a detailed idea of the way the bones are arranged and how the muscle tissues may be affecting them. It also helps assess any potential birth defects in a bit more detail.
Can you fix a fallen arch?
Non Surgical Treatment
Some of the aspects of the pain with a ?fallen arch? are related to the crushing of the joints of the outside of the foot and from the stretching of ligaments and tendons of the inside of the foot. Unfortunately, some parts of the damage from the fallen arch, the weakness in the tendons and the new shape of the foot, are not correctable without surgical reconstruction. The first goal is to stabilize the collapsed arch. This can be done through braces. If the deformity is mild, an over-the-counter arch support may be sufficient. In more severe deformities an hinged or solid ankle brace may be necessary. Rehabilitative exercises under the supervision of a physical therapist will help increase the strength of the remaining muscles. Stiffness of certain tendons including the Achilles and hamstring is also very helpful as tightness in these structures is very common in people with ?fallen arches?. Postural training is necessary. A short period of casting or walking in a cast boot will improve swelling of a recent partial tear of the tendons and ligaments on the inside of the ankle. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen, and naprosyn can help to relieve the pain, but do not heal the injuries associated with this or decrease the swelling significantly. Surgical reconstruction is available if the pain cannot be controlled reasonably with these measures.
Surgical Treatment

Common indications for surgery are cerebral palsy with an equinovalgus foot, to prevent progression and breakdown of the midfoot. Rigid and painful Pes Planus. To prevent progression, eg with a Charcot joint. Tibialis posterior dysfunction, where non-surgical treatment is unsuccessful. Possible surgical procedures include Achilles tendon lengthening. Calcaneal osteotomy, to re-align the hindfoot. Reconstruction of the tibialis posterior tendon. For severe midfoot collapse of the arch, triple arthrodesis may be indicated.
Prevention
oll away pain. If you're feeling pain in the arch area, you can get some relief by massaging the bottom of your foot. A regular massage while you're watching TV can do wonders" Stretch out. Doing the same type of stretching exercises that runners do in their warm-up can help reduce arch pain caused by a tight heel cord. One of the best exercises is to stand about three feet from a wall and place your hands on the wall. Leaning toward the wall, bring one foot forward and bend the knee so that the calf muscles of the other leg stretch. Then switch legs. Stretching is particularly important for women who spend all week in heels and then wear exercise shoes or sneakers on weekends. Get measured each time you buy new shoes. Don't assume that since you always wore a particular size, you always will. Too many people try to squeeze into their 'regular' shoe size and wind up with serious foot problems or sores on their feet. When your arch is falling, your feet may get longer or wider and you may or may not feel pain, so getting your foot measured each time you buy shoes is a good indicator of your arch's degeneration. Examine your shoes. If the heel is worn down, replace it. But if the back portion of the shoe is distorted or bent to one side, get yourself into a new pair of supportive shoes like those made specifically for walking. That's because flat feet can affect your walking stride, and failing to replace worn shoes may lead to knee or hip pain.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.

Over-pronation is very common and affects millions of Australians. To better understand this condition, we'll take a closer look at the 3 most common foot types. An estimated 70% of the population has fallen arches (or a low arch). Only 20% has a normal arch. And 10% have abnormal feet, in other words they either have flat feet or the opposite - a high arched foot.
Causes
There are many different causes of flat feet, which can be separated into two main categories. The first category, congenital flat foot, is a condition that one is born with or is predisposed to at birth. This type includes the completely asymptomatic, pediatric flexible flat foot-by far the most common form of congenital flat foot. Flexible means that an arch is present until weight is put on the foot, at which time the arch disappears. This foot type is a result of the fact that all people are born with different physical features. Some people have bigger noses than others, just as some people have flatter feet (of course, there is no known correlation between the two). Any alteration in the many building blocks of the foot can influence its shape. At the other end of the spectrum, yet within the same category of congenital flat foot, exist several rare, more severe forms of flat foot. These severe conditions include Vertical Talus, Congenital Calcaneal Valgus, and Tarsal Coalitions - all of which are more rigid (no arch with or without weight on the foot) and definitely symptomatic. Luckily, these are much less common, but can usually be identified by specialists at the time of presentation and treated appropriately. The second category, acquired flat foot, develops over time, rather than at birth. Many different factors can contribute to the development of flat feet. These include the types of shoes a child wears, a child's sitting or sleeping positions, compensation for other abnormalities further up the leg, or more severe factors such as rupture of ligaments or tendons in the foot. Very commonly, the reason for flat feet is that the foot is compensating for a tight Achilles tendon. If the Achilles tendon is tight, then it causes the foot to point down, or to plantarflex (as occurs when stepping on the accelerator of your car). Even minimal amounts of plantarflexion can simulate a longer leg on that particular side, assuming that the other foot is in the normal position. The body therefore tries to compensate by pronating, or flattening out the arch, thereby making up for the perceived extra length on the affected side.
Symptoms
People will have a very heavily dropped arch and it won?t affect them at all and people will have it slightly dropped and it could cause fierce problems. It could cause things like plantar fasciitis, it could cause heel spurs, desperate ball-of-the-foot pressure, or pressure on the big toe known as the hallux which causes discomfort in the foot. It will create problems upwards to the knees, hips and the back once you?re out of line.
Diagnosis
Podiatrists are trained in expertly assessing flat feet and identifying different risk factors and the causes for it. Initial assessment will begin with a detailed history attempting to find out if any underlying illness has resulted in this. A detailed clinical examination normally follows. The patient may be asked to perform certain movements such as walking or standing on their toes to assess the function of the foot. Footwear will also be analysed to see if there has been excessive wear or if they are contributing to the pronation of the foot. To assess the structure of the foot further, the podiatrist may perform certain x-rays to get a detailed idea of the way the bones are arranged and how the muscle tissues may be affecting them. It also helps assess any potential birth defects in a bit more detail.
Can you fix a fallen arch?
Non Surgical Treatment
Some of the aspects of the pain with a ?fallen arch? are related to the crushing of the joints of the outside of the foot and from the stretching of ligaments and tendons of the inside of the foot. Unfortunately, some parts of the damage from the fallen arch, the weakness in the tendons and the new shape of the foot, are not correctable without surgical reconstruction. The first goal is to stabilize the collapsed arch. This can be done through braces. If the deformity is mild, an over-the-counter arch support may be sufficient. In more severe deformities an hinged or solid ankle brace may be necessary. Rehabilitative exercises under the supervision of a physical therapist will help increase the strength of the remaining muscles. Stiffness of certain tendons including the Achilles and hamstring is also very helpful as tightness in these structures is very common in people with ?fallen arches?. Postural training is necessary. A short period of casting or walking in a cast boot will improve swelling of a recent partial tear of the tendons and ligaments on the inside of the ankle. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen, and naprosyn can help to relieve the pain, but do not heal the injuries associated with this or decrease the swelling significantly. Surgical reconstruction is available if the pain cannot be controlled reasonably with these measures.
Surgical Treatment

Common indications for surgery are cerebral palsy with an equinovalgus foot, to prevent progression and breakdown of the midfoot. Rigid and painful Pes Planus. To prevent progression, eg with a Charcot joint. Tibialis posterior dysfunction, where non-surgical treatment is unsuccessful. Possible surgical procedures include Achilles tendon lengthening. Calcaneal osteotomy, to re-align the hindfoot. Reconstruction of the tibialis posterior tendon. For severe midfoot collapse of the arch, triple arthrodesis may be indicated.
Prevention
oll away pain. If you're feeling pain in the arch area, you can get some relief by massaging the bottom of your foot. A regular massage while you're watching TV can do wonders" Stretch out. Doing the same type of stretching exercises that runners do in their warm-up can help reduce arch pain caused by a tight heel cord. One of the best exercises is to stand about three feet from a wall and place your hands on the wall. Leaning toward the wall, bring one foot forward and bend the knee so that the calf muscles of the other leg stretch. Then switch legs. Stretching is particularly important for women who spend all week in heels and then wear exercise shoes or sneakers on weekends. Get measured each time you buy new shoes. Don't assume that since you always wore a particular size, you always will. Too many people try to squeeze into their 'regular' shoe size and wind up with serious foot problems or sores on their feet. When your arch is falling, your feet may get longer or wider and you may or may not feel pain, so getting your foot measured each time you buy shoes is a good indicator of your arch's degeneration. Examine your shoes. If the heel is worn down, replace it. But if the back portion of the shoe is distorted or bent to one side, get yourself into a new pair of supportive shoes like those made specifically for walking. That's because flat feet can affect your walking stride, and failing to replace worn shoes may lead to knee or hip pain.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.




 Morton's Neuroma is a common foot problem associated with pain, swelling and/or an inflammation of a nerve, usually at the ball-of-the-foot between the 3rd and 4th toes. Symptoms of this condition include sharp pain, burning, and even a lack of feeling in the affected area. Morton's Neuroma may also cause numbness, tingling, or cramping in the forefoot.
Morton's Neuroma is a common foot problem associated with pain, swelling and/or an inflammation of a nerve, usually at the ball-of-the-foot between the 3rd and 4th toes. Symptoms of this condition include sharp pain, burning, and even a lack of feeling in the affected area. Morton's Neuroma may also cause numbness, tingling, or cramping in the forefoot.




 Overview
Overview Symptoms
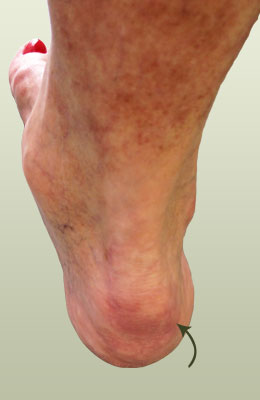
Symptoms A bunion, also known by its medical name hallux abductovalgus, is foot condition in which your big toe points toward your second toe, causing a bump or prominence to develop on the inside edge of your big toe and first metatarsal bone. Your first metatarsal bone is the long bone located directly behind your big toe, in your mid-foot. A bunion will cause your forefoot to appear wider because the base of your big toe now points away from your foot instead of pointing straight ahead.
A bunion, also known by its medical name hallux abductovalgus, is foot condition in which your big toe points toward your second toe, causing a bump or prominence to develop on the inside edge of your big toe and first metatarsal bone. Your first metatarsal bone is the long bone located directly behind your big toe, in your mid-foot. A bunion will cause your forefoot to appear wider because the base of your big toe now points away from your foot instead of pointing straight ahead.
